Last Updated on June 25, 2024
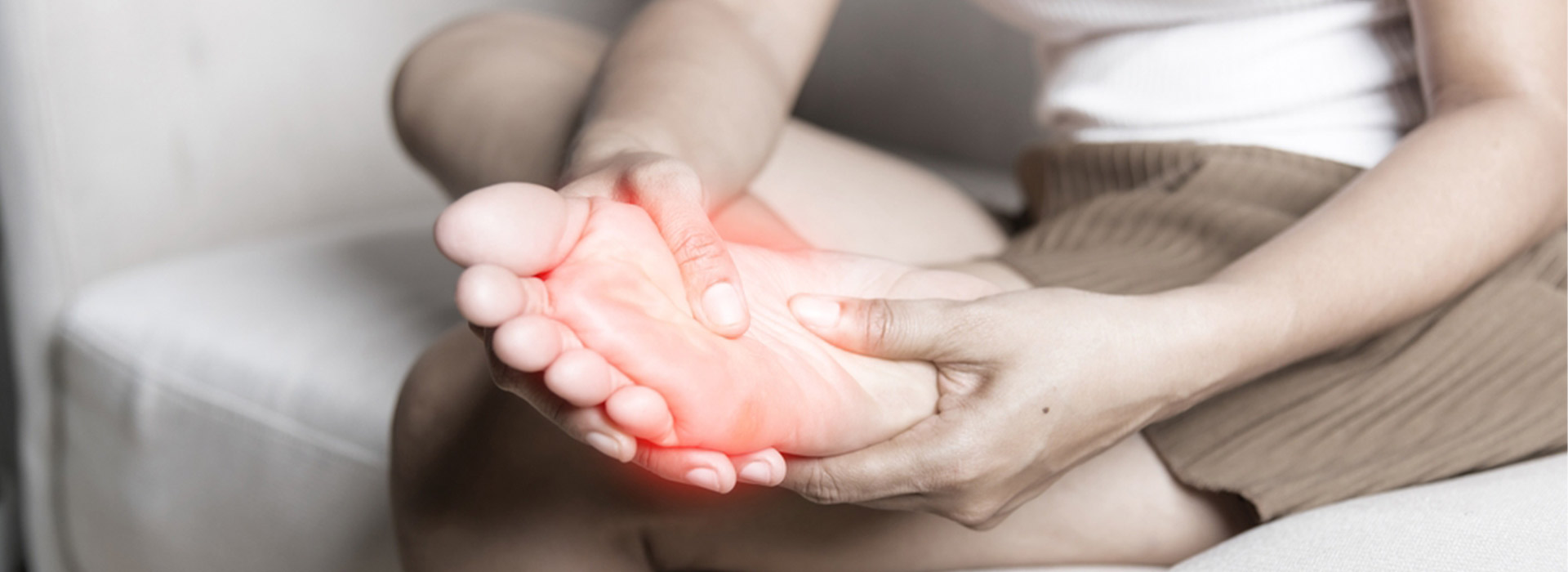
Diabetic neuropathy refers to nerve damage that may develop in individuals diagnosed with diabetes. Over time, high blood sugar levels can injure nerves throughout your body, but diabetic neuropathy most often damages nerves in your legs and feet. According to the American Diabetes Association, approximately 50% of people with diabetes will experience some form of neuropathy during their lifetime. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that as of 2021, around 38.4 million Americans have diabetes, highlighting the significant impact and prevalence of diabetic neuropathy. This widespread issue not only causes discomfort and pain but also increases the risk of severe complications, including foot ulcers and amputations. Therefore, diabetic neuropathy self-care plays a crucial role in managing this condition and improving the quality of life for those affected. This blog will explore effective self-care managing diabetic neuropathy.
All About Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a common and serious complication of diabetes, hence, diabetic neuropathy self-care essential. The primary cause is prolonged exposure to high blood glucose levels, which can damage the nerves and the small blood vessels that supply them with oxygen and nutrients. Symptoms of diabetic neuropathy can vary, but they often include:
- Numbness or reduced ability to feel pain or temperature changes
- Tingling or burning sensations
- Sharp pains or cramps
- Muscle weakness
- Loss of reflexes, especially in the ankle
- Loss of balance and coordination
Knowing the types of diabetic neuropathy is essential for effective diabetic neuropathy self-care. These include:
- Peripheral Neuropathy: The most common type, affecting the feet and legs, and sometimes the hands and arms.
- Autonomic Neuropathy: Affects the autonomic nerves that control internal organs.
- Proximal Neuropathy: Affects nerves in the thighs, hips, or buttocks, leading to weakness in the legs.
- Focal Neuropathy: Sudden weakness of one nerve or a group of nerves, causing muscle weakness or pain.
Self-Care Managing Diabetic Neuropathy
1. Blood Sugar Control
The most crucial aspect of diabetic neuropathy self-care is keeping blood sugar levels within the target range. This can help prevent further nerve damage and may even improve symptoms. Key strategies include:
- Regular Monitoring: Check blood glucose levels as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Medication Adherence: Take insulin or oral diabetes medications as prescribed.
- Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid high-sugar and high-fat foods.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activities like walking, swimming, or biking. Exercise helps to control blood sugar levels, improve circulation, and maintain a healthy weight.
2. Foot Care
Peripheral neuropathy often affects the feet, so proper foot care is essential to prevent complications such as ulcers and infections:
- Daily Inspection: Check your feet daily for cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, or other signs of injury.
- Cleanliness: Wash your feet daily with lukewarm water and mild soap. Dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes.
- Moisturize: Apply lotion to your feet to prevent dryness and cracking, but avoid the areas between the toes to prevent fungal infections.
- Proper Footwear: Wear well-fitting shoes and socks. Avoid walking barefoot, even indoors.
- Regular Podiatrist Visits: Have your feet examined by a podiatrist regularly.
Also Read: Ticklish Feet: A Curious Quirk
3. Pain Management
Managing pain associated with diabetic neuropathy is vital for maintaining quality of life and is a crucial step for self-care managing diabetic neuropathy. Various strategies can be employed:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription medications, and topical treatments may be used to manage pain.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and therapies designed to strengthen muscles and improve mobility.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, biofeedback, and other alternative treatments can help manage pain.
- Relaxation Techniques: Stress reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can also help alleviate pain.
Also Read: Diabetes Swollen Feet: Causes & Treatments
4. Lifestyle Modifications
Incorporating healthy lifestyle habits is crucial for self-care management of diabetic neuropathy:
- Quit Smoking: Smoking narrows and hardens arteries, reducing blood flow to the legs and feet, which can worsen neuropathy symptoms.
- Limit Alcohol: Excessive alcohol can exacerbate nerve damage and worsen symptoms.
- Balanced Diet: Maintain a diet that supports overall health, focusing on nutrient-rich foods that support nerve health.
Also Read: Is Feeling Sleepy After Eating A Sign Of Diabetes?
5. Regular Medical Checkups
Regular checkups with healthcare providers are important for diabetic neuropathy self-care and its complications. During these visits:
- Review Blood Sugar Levels: Discuss your blood sugar levels and any necessary adjustments to your management plan.
- Examine Feet and Skin: Your doctor will check for any signs of complications.
- Monitor Medications: Ensure that medications for pain management, blood sugar control, and other conditions are effective and properly adjusted.
6. Educate Yourself
Education is a powerful tool in self-care managing diabetic neuropathy. Understanding the condition, recognizing symptoms, and being aware of the best self-care practices empower patients to take control of their health.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest information on diabetes management.
- Support Groups: Join support groups to share experiences and gain insights from others who have diabetic neuropathy.
7. Mental Health Care
Living with chronic pain and other symptoms of diabetic neuropathy can impact mental health, highlighting the importance of managing stress and emotional well-being as an integral aspect of diabetic neuropathy self-care.
- Counseling: Seek counseling or therapy to help cope with the emotional impact of the condition.
- Support Network: Rely on family, friends, and support groups for emotional support.
- Stress Management: Engage in activities that reduce stress, such as hobbies, exercise, and relaxation techniques.
Call to Action
Effective diabetic neuropathy self-care is paramount for managing this condition and significantly enhancing the quality of life for those affected. By consistently monitoring blood sugar levels, implementing meticulous foot care practices, effectively managing pain, embracing a wholesome lifestyle, and staying abreast of the latest developments, individuals can proactively address their condition. Regular medical checkups, coupled with addressing mental health needs, serve as integral components of a comprehensive diabetic neuropathy self-care regimen. Through these multifaceted strategies, individuals grappling with diabetic neuropathy can navigate their symptoms more effectively and cultivate a lifestyle marked by increased vitality and fulfillment. Don’t miss the opportunity to participate in the ongoing study on diabetic peripheral neuropathy conducted by Prime Revival Research Institute. Enroll now!

