Last Updated on February 1, 2024
Introduction
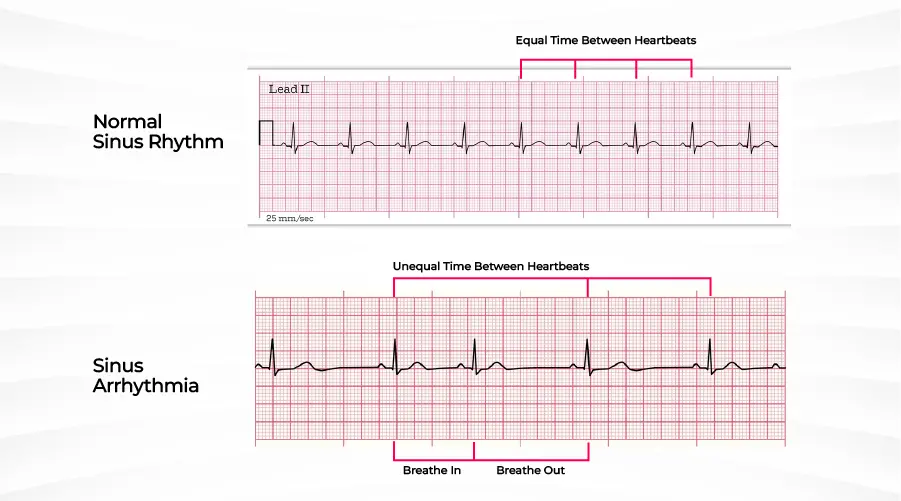
Before asking “what is sinus arrhythmia?” we should know about the normal sinus rhythm. A normal sinus rhythm (NSR) is a rhythm that originates in the sinus node and has the same frequency as a normal heartbeat. The rate of the normal sinus rhythm varies according to the inputs from the nervous system.
In this article, we will try to find out the answer to some of the following common questions:
- Is sinus arrhythmia normal?
- Is it serious?
- Sinus arrhythmia causes?
- What does its EKG show?
- What are its common symptoms?
- And most importantly, what is sinus arrhythmia?
The Normal Sinus Heart Rate
The normal heart rate is anywhere between 60 to 100 beats per minute at rest. The range can be between 43 and 102 beats per minute in men and 47 to 103 beats per minute in females. In infants, the normal rate is 110 to 150 beats per minute, with a gradual decline as age increases up to 60 years. Pharmacological and physiological changes can be sinus arrhythmia causes.
What is Sinus Arrhythmia?
Despite its name, sinus arrhythmia is not related to the sinus cavities in the face but rather to the sinoatrial or sinus node located in the upper chamber on the right side of the heart, specifically in the right atrium. The sinus node serves as the heart’s natural pacemaker, determining the rhythm of heartbeats. Normal sinus rhythm is a regular pattern observed in generally healthy individuals, while sinus arrhythmia is a type of abnormal heart rhythm, where the time between heartbeats may slightly vary depending on whether a person is inhaling or exhaling. Sinus arrhythmias can be manifested as:
- Sinus tachycardia, is characterized by a heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute.
- Sinus bradycardia, marked by a heart rate slower than 60 beats per minute.
Different types of Sinus Arrhythmia
The most prevalent and harmless version is respiratory sinus arrhythmia in which the heart rate fluctuates with breathing. When a person breathes in, the heart rate rises. In contrast, when the person breathes out, it decreases. This type is a physiological response and is not an abnormality. It usually affects children the most and its incidence decreases with age. The exact cause is unknown but, it is believed to be a result of pulmonary and vascular reflexes. It is common in very heavy breathers.
The other form is no respiratory sinus arrhythmia (NRSA). It is more likely to occur in people who have taken digoxin or have other heart conditions. NSRA is more common in adults. Again, the exact cause remains unknown.
One another form of sinus arrhythmia is known as ventriculophasic sinus arrhythmia, which is associated with third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block in individuals.
This disease is known to express itself when the heart rate is slow. On the other hand, as a person exercises or does strenuous activity, the heart rate rises and becomes regular.
Sinus Arrhythmia Causes
To understand the sinus arrhythmia causes, it may be useful to learn how the heart typically beats.
The heart has four compartments — two upper chambers called atria and two lower chambers known as ventricles. The electrical impulse for the rhythm of the heart typically originates in the sinus node present in the upper right atrium. These electrical signals travel across the heart from the atria to the ventricles causing contraction of the heart. The pace of the heart contraction changes according to activity, emotions, or other factors and can be fast or slow.
Sinus arrhythmia causes can include the following:
- Age-related wear and tear of heart tissues
- Damage to the sinus node
- Heart disease
- Inflammatory diseases affecting the heart
- Medications to treat high blood pressure, including calcium channel blockers and beta blockers
- Medications to treat irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias)
- Some Alzheimer’s disease medications
- Neuromuscular diseases, such as muscular dystrophy
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Rare genetic changes
Symptoms
Sinus arrhythmia causes complications very rarely. The condition is likely to go undiscovered because it rarely causes any issues.
Common signs and symptoms may include:
- Rapid and fluttering heartbeats (palpitations)
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Confusion
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fainting or near fainting
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Slower pulse (bradycardia)
Complications
This disease rarely causes serious effects and usually goes unnoticed. However, complications may depend on other factors. The four major complications are:
- Atrial fibrillation
- Heart failure
- Stroke
- Cardiac arrest
Risk factors
This disorder can occur at any age but is most common in older people. The risk factors coincide with the risk factors for other heart diseases including:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Excess body weight
- Lack of exercise
What is ECG with Sinus Arrhythmia?
The most common and effective method of diagnosing arrhythmia is through an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). You may need further testing if the EKG does not identify the anomaly.
Your doctor generally looks to answer these questions when he sees your EKG:
- Is there a P wave?
- Is each P wave the same shape?
- Is each P wave followed by a QRS complex?
- Is the P-R interval between 3-5 small squares?
- Is the rhythm regular?
During an EKG test, you wear a portable EKG recording device for 24 hours or more. This is known as the Holter monitor. In some cases, people may have to wear this monitor for up to 2 weeks.
The three common findings on an EKG are:
- Irregular heart rate
- Greater than 0.12 seconds variation in the RR interval
- Monoform P waves
It is a good idea to have a copy of your EKG and discuss it with your cardiologist or keep a copy for the future.
Other tests used in diagnosing arrhythmias include:
- Cardiac event recorder: A special device that records occasional symptoms over longer durations.
- Electrophysiological (EP) Study: It is a test in which soft wires pass through larger veins into the heart.
- Echocardiogram (Echo): An echo is an ultrasound scan of your heart.
With an EKG result, your doctor rules out the following cardiac disorders:
- Atrial fibrillation
- Atrial flutter
- Multifocal atrial tachycardia
- Premature atrial contractions (PAC)
- Premature ventricular contractions (PVC)
- Bradyarrhythmia
Treatment for Sinus Arrhythmia
Treatment is typically unnecessary for sinus arrhythmia since it is a common and benign occurrence that does not give rise to additional complications. Most individuals with sinus arrhythmia do not require intervention, and the condition may naturally become less detectable as children and young adults mature.
The Takeaway
This blog aimed to answer the question “What is sinus arrhythmia?”. While there can be many causes, most of them are unavoidable. You might become worried if your EKG shows abnormalities, but you need to understand that it might be an indication of a healthy heart. This is why it is important to always consult your cardiologist and ask questions that concern you.
Prime Revival Research Institute is investigating novel treatments for Sinus arrhythmia. You may want to explore all possible options before you begin treatment.