Last Updated on February 26, 2024
 Introduction
Introduction
Peripheral Neuropathy is a debilitating condition that may affect one’s day-to-day routine. There are around 20 million people in the US who suffer from some form of peripheral neuropathy. For veterans who are grappling with the challenges of peripheral neuropathy, understanding the VA rating for peripheral neuropathy is crucial for securing the compensation they deserve.
In this blog post, we will unlock the mysteries of peripheral neuropathy and the VA rating process and provide key insights into how the VA decides disability ratings, aiming to make it easier for veterans to navigate and understand the system.
What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that manifests when the nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord sustain damage. These nerves are responsible for sending information from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. When damage occurs to these nerves, it disrupts communication between the brain and the body, causing symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness, and severe foot issues, including ulcers and infections.
Every nerve in the body has a distinct role, and the symptoms encountered by a veteran depend on the specific nerves affected. There are various nerve types, including sensory, motor, and autonomic. Autonomic nerves oversee bodily systems and activities like blood pressure, digestion, heart rate, and urination. Sensory nerves manage sensation, while motor nerves regulate muscle movement. Peripheral neuropathy mainly affects the nerves in the hand, feet, legs, and arms.
Factors Contributing to VA Rating for Peripheral Neuropathy
Veterans may develop peripheral neuropathy due to a range of factors encountered during their active duty, including:
- Traumatic injuries
- Exposure to infections
- Contact with toxins such as exposure to Agent Orange
These situations, prevalent in military service, can serve as key contributors to the onset of peripheral neuropathy.
Furthermore, diabetes, a prevalent cause of this condition, is frequently linked to aspects of military service. This emphasizes the significance of considering these diverse factors in the VA rating for peripheral neuropathy. Additionally for veterans in Texas there is a hopeful news, clinical trials for diabetic peripheral neuropathy are underway, offering a potential avenue for improved treatments and management strategies.
Is Peripheral Neuropathy Considered a Disability by VA?
While the VA lacks a precise diagnostic code exclusively for peripheral neuropathy, the condition is indeed considered for VA ratings based on the affected nerves.
Let’s delve into the intricacies of how and what considerations are made during the VA rating for peripheral neuropathy.
What is VA Rating for Peripheral Neuropathy?
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) employs a standardized system for rating disabilities, also known as the VA Disability Rating for peripheral neuropathy, to determine how much compensation a veteran is entitled to for their service-connected disabilities. VA ratings, ranging from 0% to 100%, determine the compensation level a veteran receives based on disability severity. Ratings increase in increments of 10%, with higher ratings correlating to higher compensation.
Generally, the lowest VA rating for peripheral neuropathy is 10% while the highest VA rating is 40%. A rating higher than 40% is possible if your peripheral neuropathy has caused severe functional impairment.
What Factors will be Considered by the VA Rating Scale for Peripheral Neuropathy?
The factors that will be considered by VA rating peripheral neuropathy are:
- Sensory Loss: This refers to any loss of sensation in the affected areas. The VA will evaluate the extent of sensory loss to determine the severity of your peripheral neuropathy.
- Motor Nerve Damage: This refers to any damage to the nerves that control muscle movements. The VA will evaluate the severity of motor nerve damage and how it affects your ability to move and perform daily tasks.
- Reflexes: The VA will also evaluate your reflexes, as damage to the peripheral nerves can affect reflexes and muscle responses.
- Muscle Atrophy: Muscle atrophy refers to the shrinking or wasting of muscles due to nerve damage. The VA will assess the degree of muscle atrophy to determine the severity of your peripheral neuropathy.
To qualify for service-connected benefits, veterans must establish that their symptoms meet the criteria outlined in the VA rating for peripheral neuropathy. This includes demonstrating specific nerve damage, such as impairment in the peroneal, sciatic, or femoral nerves, aligning with the stipulated guidelines for evaluation.
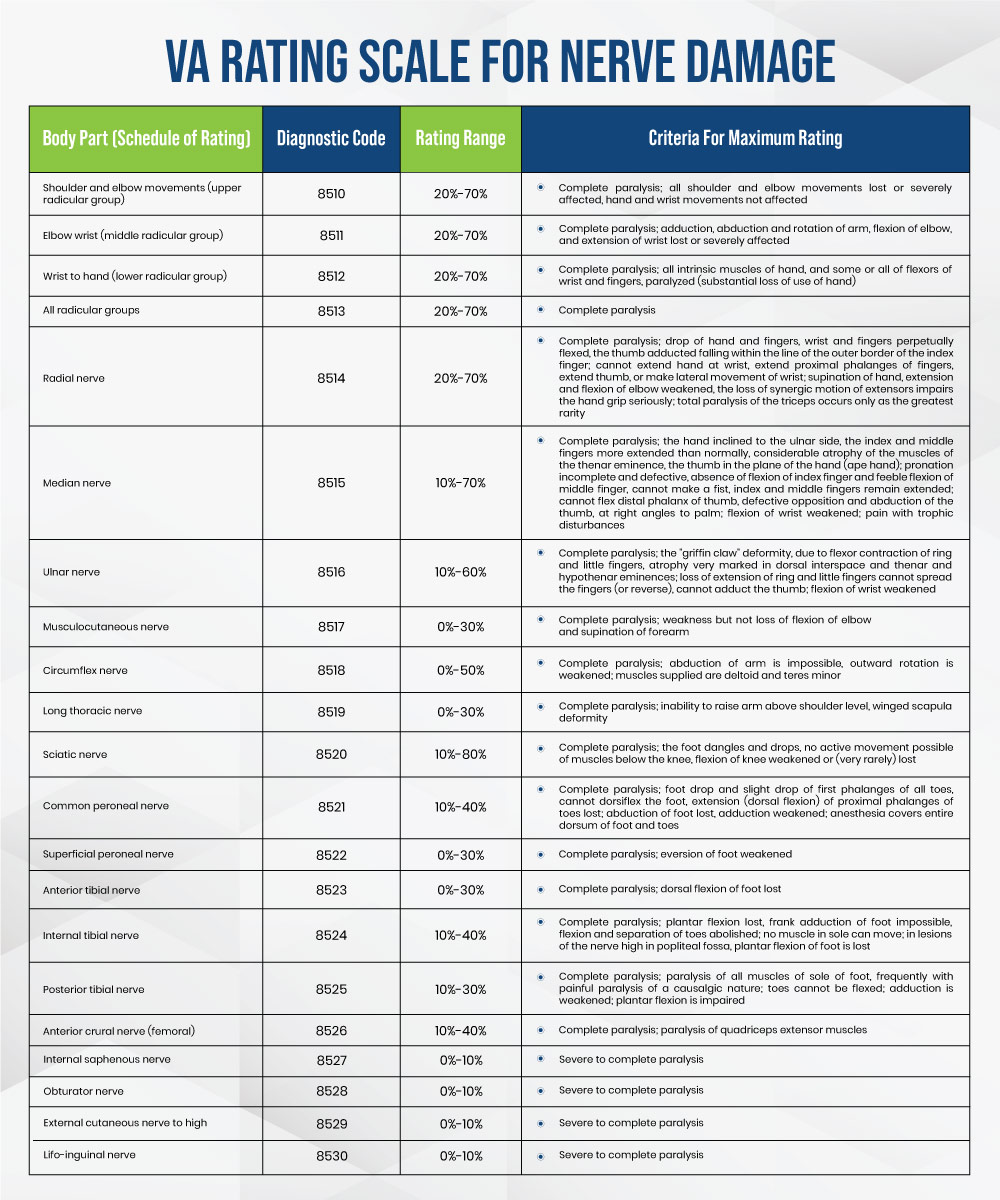
Let’s dive into one example and understand the VA rating process for common peroneal nerve damage:
The common peroneal nerve, which originates from the lumbar and sacral spine regions as part of the sciatic nerve, receives a rating under diagnostic code 8521. If a veteran experiences symptoms such as the ones mentioned below, they may be eligible for benefits:
- Foot drop
- Sagging of the segments of each toe
- Inability to raise the foot from the ankle
- Loss of movement of the toes
Hence, based on the VA rating for peripheral neuropathy, the veteran may be eligible for the maximum 40% rating for each affected extremity within the designated category. If the damage doesn’t qualify for a 40% VA rating for peripheral neuropathy, veterans need to show incomplete paralysis at three levels of severity:
- Severe (30%)
- Moderate (20%)
- Mild (10%)
This helps the doctor accurately decide how severe the condition is for VA rating purposes.
VA Rating for Peripheral Neuropathy: Challenges in Diagnosis
VA rating for peripheral neuropathy often involves undergoing specific tests such as:
- Routine neurological examinations during check-ups
- Electromyography (EMG) tests
- Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) tests
- Biopsies
Proving peripheral neuropathy can be challenging initially due to potential misdiagnosis or lack of diagnosis. Various factors contribute to this challenge, such as:
- Intermittent symptoms
- Veterans not reporting issues
- Assuming symptoms are part of the aging process
An unfortunate reason for the difficulty in diagnosing peripheral neuropathy is:
- Some veterans hesitate to seek medical attention because they fear being perceived as chronic complainers.
- Delayed-onset peripheral neuropathy, developing years after service, adds another layer of complexity to the diagnosis
Whether peripheral neuropathy is undiagnosed or misdiagnosed, the result is the same—deserving veterans miss out on entitled benefits. It is crucial for veterans to seek medical attention for neuropathy, including the necessary tests for accurate diagnosis and severity rating for VA benefits.
Also Read: Your Guide To Diabetic Nerve Pain Symptoms
Takeaway
In conclusion, peripheral neuropathy is a condition that affects the extremities and nerves throughout the body. The VA rates peripheral neuropathy by conducting tests to determine the compensation amount for veterans affected by this nerve condition. It can be tricky due to potential misdiagnosis or veterans not reporting symptoms. Delayed-onset neuropathy, appearing years later, makes it even more challenging. The key takeaway is that accurate diagnosis and communication with doctors are vital. This ensures veterans get the rightful benefits they deserve through the VA rating processLet’s dive into one example and understand the VA rating process for common peroneal nerve damage:

 Introduction
Introduction